I am a computational research scientist and software engineer at Flatiron Institute's Center for Computational Astrophysics, part of the Simons Foundation. My work focuses on developing scalable, high-performance multiphysics simulation software, with a growing emphasis on integrating modern AI techniques and automatic differentiability. Before joining the Flatiron Institute, I was a Computational Physicist at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, where I specialized in designing high-order Arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian (ALE) finite element methods for magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) simulations on heterogeneous computing architectures, as part of the Multiphysics on Advanced Platforms Project (MAPP). In addition to my work in computational astrophysics and multiphysics methods, I have a strong research interest in cosmological simulations, particularly modeling alternative dark matter candidates such as fuzzy dark matter.
I earned my Ph.D. in Astrophysics from Harvard University in 2017, where I was advised by Lars Hernquist. During my doctoral research, I developed a finite-volume moving mesh magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) algorithm, which I applied to study structure formation and magnetic field amplification in both the interstellar medium and cosmological environments. I integrated my solvers into the Arepo simulation code. Prior to my Ph.D., I received an A.B. in Mathematics and Astrophysics from Harvard in 2012.
My research interests span multiphysics simulations, cosmology, galaxy formation and evolution, black hole physics, turbulence, numerical methods, scientific visualization, and the integration of machine learning and AI into computational astrophysics.
Originally from Hawaii, I enjoy spending time outdoors when away from the computer.
📝 I maintain a blog featuring introductory tutorials on scientific computing with Python, accessible at the undergraduate level. You can follow my posts on Medium and Twitter.








Download my curriculum vitae (CV) [.pdf]
Cosmological Structure Formation and Soliton Phase Transition in Fuzzy Dark Matter with Axion Self-Interactions
Mocz, P.; Fialkov, A.; Vogelsberger, M.; Boylan-Kolchin, M; Chavanis, P.H.; Amin, M.A.; Bose, S.; Dome, T.; Hernquist, L.; Lancaster, L.; Notis, M.; Painter, C.; Robles, V.H.; Zavala, J.; 2023 MNRAS, 521, 2608
Toward Cosmological Simulations of Dark Matter on Quantum Computers
Mocz, P.; Szasz, A.; 2021 ApJ, 910, 29
Galaxy Formation with BECDM - II. Cosmic Filaments and First Galaxies
Mocz, P.; Fialkov, A.; Vogelsberger, M.; Becerra, F.; Shen, X.; Robles, V.H.; Amin, M.A.; Zavala, J.; Boylan-Kolchin, M.; Bose, S.; Marinacci, F.; Chavanis, P.H.; Lancaster, K.; Hernquist, L.; 2021 MNRAS, 494, 2021
First star-forming structures in fuzzy cosmic filaments
Mocz, P.; Fialkov A.; Vogelsberger, M.; Becerra, F.; Amin, M.A.; Bose, S.; Boylan-Kolchin, M.; Chavanis, P.H.; Hernquist, L.; Lancaster, L.; Marinacci, M.; Robles, V.H.; Zavala, J; 2019 Phys. Rev. Lett. (Editors' Selection) 123, 14

A Markov model for non-lognormal density distributions in compressive isothermal turbulence
Mocz, P.; Burkhart, B.; 2019 ApJL, 884, 2
Formation, Gravitational Clustering and Interactions of Non-relativistic Solitons in an Expanding Universe
Amin, M.; Mocz, P.; 2019 Phys. Rev. D, 100, 6
Star formation from dense shocked regions in supersonic isothermal magnetoturbulence
Mocz, P.; Burkhart, B.; 2018 MNRAS, 480, 3916
On the Schrodinger-Poisson--Vlasov-Poisson correspondence
Mocz, P.; Lancaster, L.; Fialkov A.; Becerra, F.; Chavanis, P.H.; 2018 PhRvD, 97, 3519
Galaxy Formation with BECDM - I. Turbulence and relaxation of idealised haloes
Mocz, P.; Vogelsberger, M.; Robles, V.; Zavala J.; Boylan-Kolchin, M.; Fialkov A.; Hernquist, L.; 2017 MNRAS, 471, 4559
Moving mesh simulations of star forming cores in magneto-gravo-turbulence
Mocz, P.; Burkhart, B.; Hernquist, L.; McKee, C.; Springel, V.; 2017 ApJ, 838, 1
Interested in scientific computing? Check out my ~100 line Python tutorials on computational astro/physics at https://philip-mocz.medium.com/
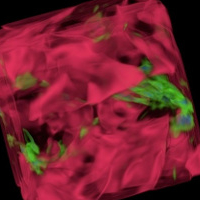
PAVOREAL (PArellel VOlume REndering ALgorithm) on GPUs

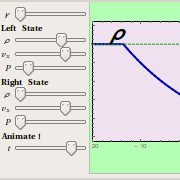
Explore the shock structure in the Euler and MHD Riemann problems

Paper on my simulations of a cosmic-ray pressure gradient instability in a turbulent MHD environment at a shock interface, as part of my project for Astronomy 253 (plasma physics). Read the report (.pdf) and download the Matlab code
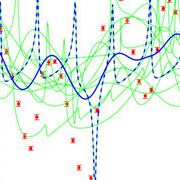
Bayesian nested sampling fitting of exoplanet radial velocity curve with 2 planets
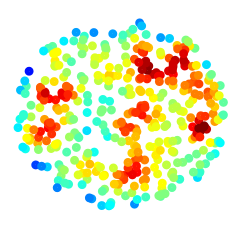
A simple introduction (.pdf) to smoothed-particle hydrodynamics (SPH), and writing your own code

Computational Physicist
 orcid.org/0000-0001-6631-2566
orcid.org/0000-0001-6631-2566
Philip Mocz pronounced: